Ovid is a database searching platform that facilitates access to four main research databases at Monash Health; Medline, Embase, Emcare and PsycINFO. The search functions in Ovid allow for systematised searches to be conducted, saved and rerun through each of the databases.
Why is database searching important?
Step-by-step worksheet
Use the Library's worksheet to write your search strategy. The appendix includes real-world examples.
Worksheet - Literature Searching: Step by step
How to Search in Ovid
Watch the video below for full instructions from our comprehensive webinar on searching using Ovid. Covers field codes, truncation, wildcards, adjacency, subject headings and translating across Ovid databases.
Shortcuts for efficient searching on Ovid
Incorporating these shortcuts into your keywords can help you to search efficiently for spelling variations and differences in phrasing. Click here to open a PDF version of the table.

Note: These 'shortcuts' are known as search operators or syntax. They are, in effect, a language that we can use to 'talk' to search platforms and databases. Different search platforms and databases speak in slightly different languages. See the Quick reference syntax table below for more information.
Translating a search between Ovid databases:
Searching in multiple databases is best practice for any literature review. If you have already created a search, adjust the search to recreate the search strategy in another database to access studies that are also relevant. For full instructions on how to translate a Medline search into an Embase search watch the video below.
Apply limits in Ovid
In Ovid databases -- MEDLINE, Embase, Emcare, and PsycINFO -- common limit options are found beneath the search bar. Click on the 'Additional Limits' button to open further limit options, such as clinical queries, publication types, and age groups.
Recommended Resources:
Cochrane Library contains the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials. It is considered the leader in the production and publishing of systematic reviews. When searching for quality evidence, the Cochrane database allows access to high quality evidence with a range of searching styles.
Why is searching in Cochrane important?
How to search in Cochrane
Watch the video below for the comprehensive webinar on searching using Cochrane. Covers advanced searching, using the search manager, PICO searching and managing results.
Translating a search to Cochrane:
Searching in multiple databases is best practice for any literature review. If you have already created a search, use the same search strategy in Cochrane to access studies that are also relevant. For full instructions on how to translate a Medline search into a Cochrane search watch the video below.
Apply limits in Cochrane
In Cochrane Library, click the 'Limit' button on the final search line to open limit options such as content type (review, trial, protocol) and publication date.
Alternatively, view your search results and select from the 'Filter your results' menu to the left. The publication date filter is shown as one example.
Recommended Resources:
A wide range of other medical research databases exist, varying in scope from broad multidisciplinary coverage to highly specialized collections tailored to specific fields or professions. These resources can complement core databases by offering unique content, regional perspectives or discipline-specific literature not indexed elsewhere.
Why is searching in other databases important?
Searching shortcuts in databases:
Databases use different shortcuts and symbols. When searching in each database check that you are using the right symbols. Use the quick reference table below to find the right symbol.
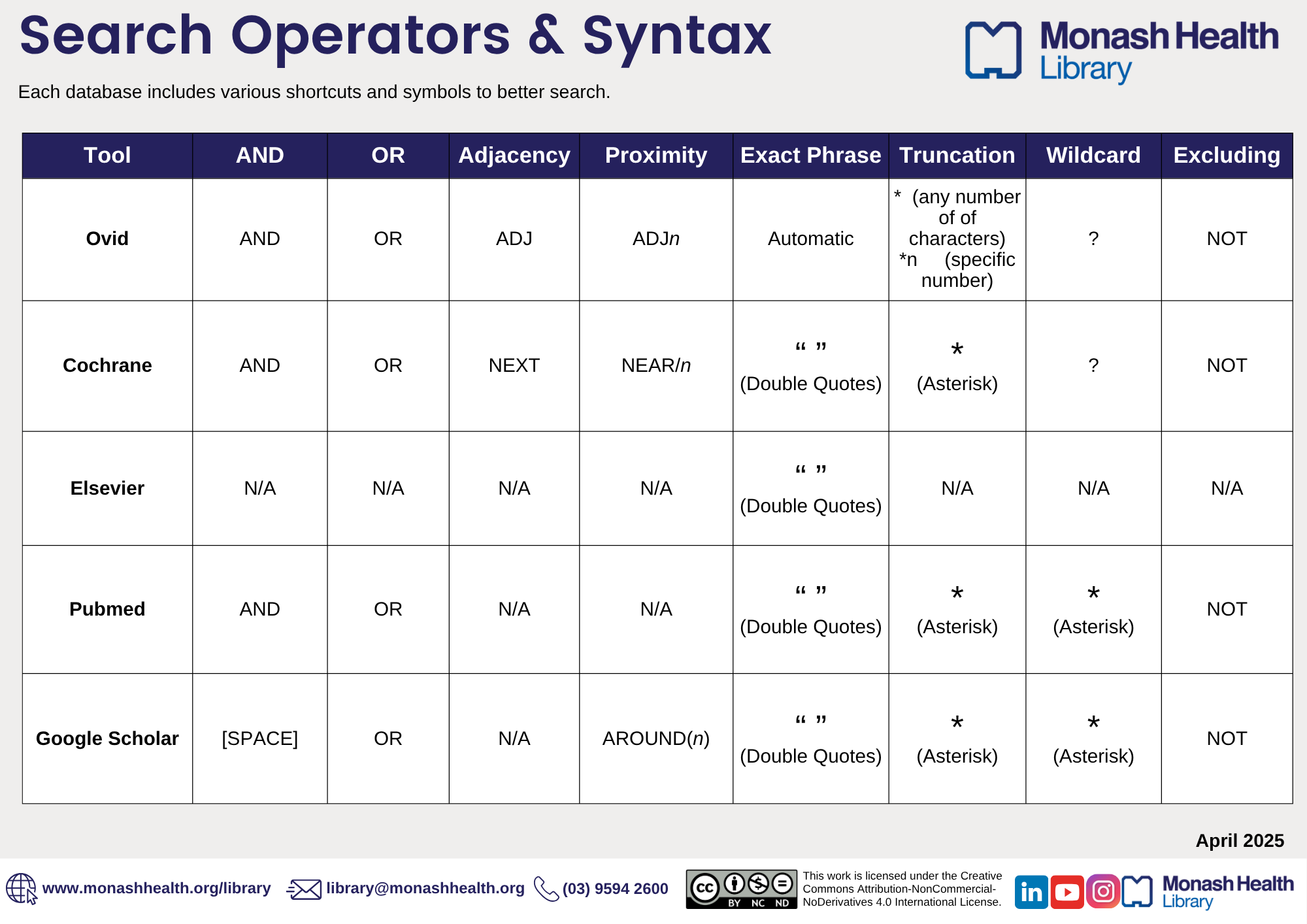
Apply limits in other databases
In many other databases, limits or filters are found along the left-hand side of your search results.
The Library's Databases for Literature Searching page has user guides for a wide range of other databases.
Examples
Recommended Resources

